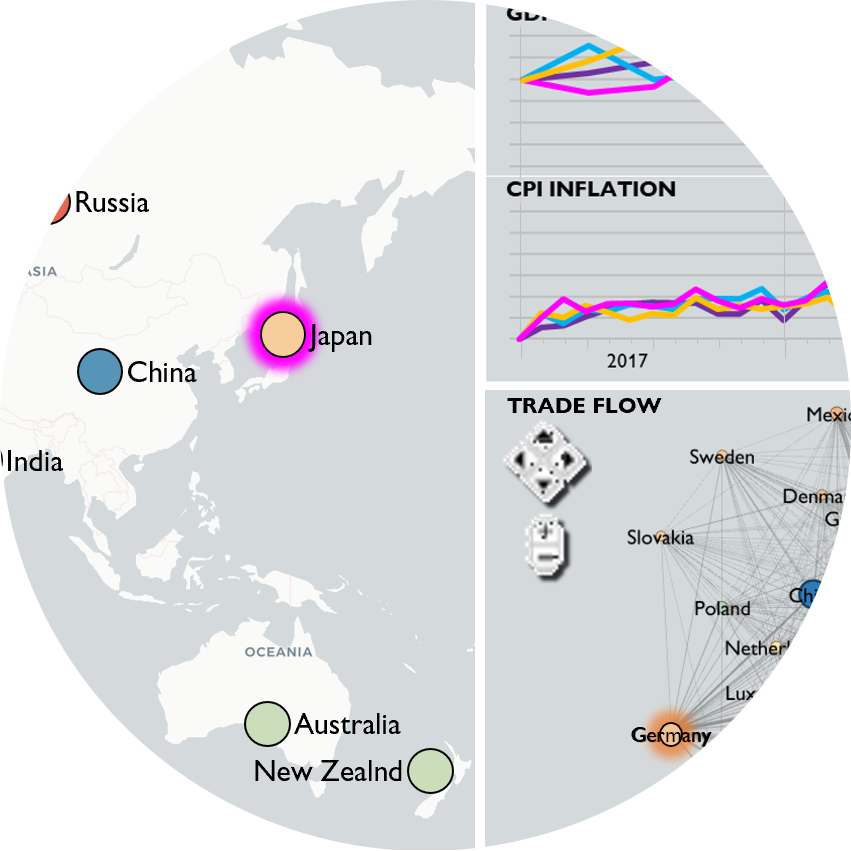
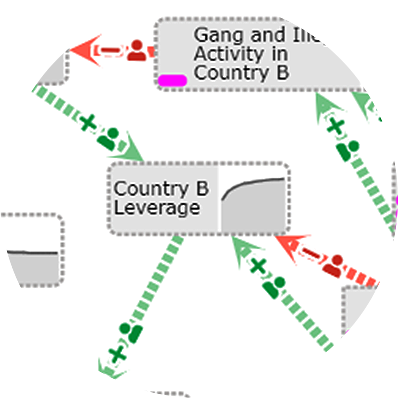
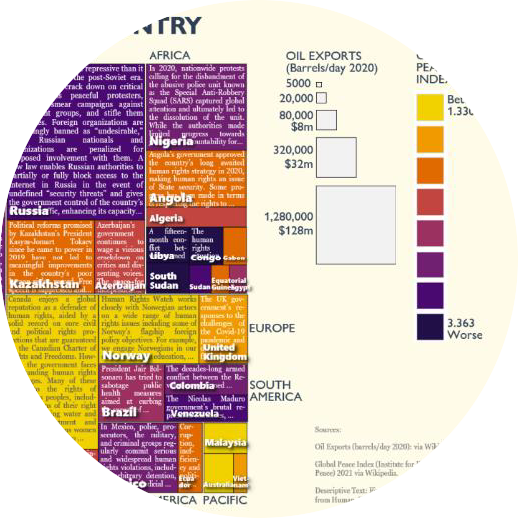
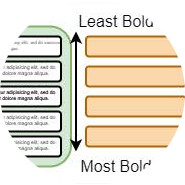
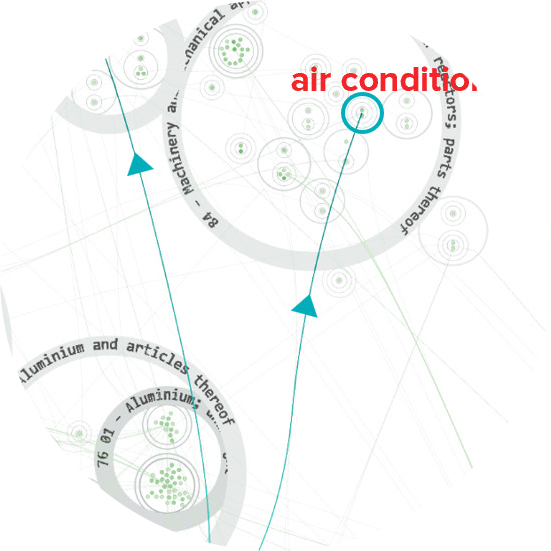
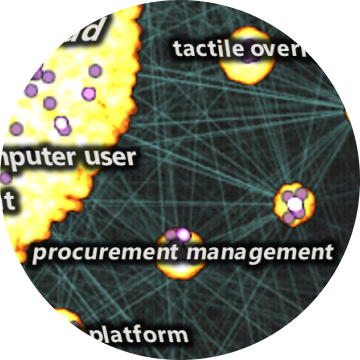
In an age of Large Language Models, online misinformation, plagiarism, hate speech, and more—the analysis of text is increasingly important. But traditional statistical visualization tools have lagged behind. Visualizing with Text characterizes the design-space for directly integrating and visualization to reveal information disparity with examples such as text-centric scatterplots, line charts, treemaps, mindmaps and tables.
Field
Visualization Theory
2024
-
-
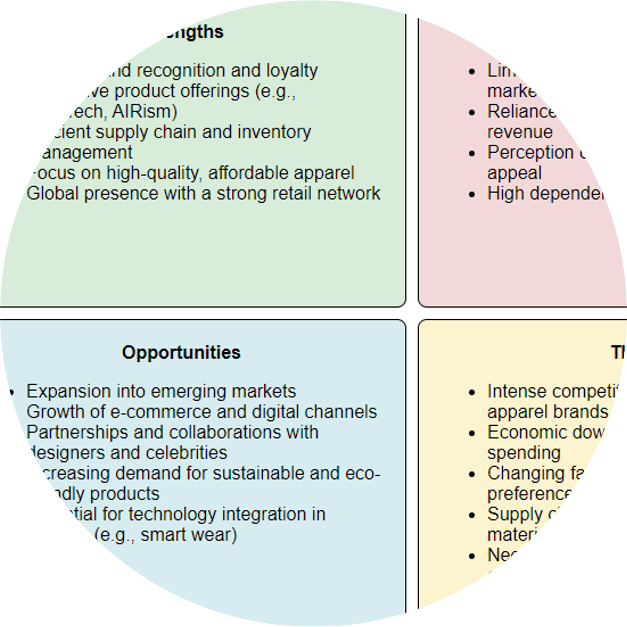
Strategy management analyses are created by business consultants with common analysis frameworks (i.e. comparative analyses) and associated diagrams. We show these can be largely constructed using LLMs, starting with the extraction of insights from data, organization of those insights according to a strategy management framework, and then depiction in the typical strategy management diagram for that framework (static textual visualizations).
-
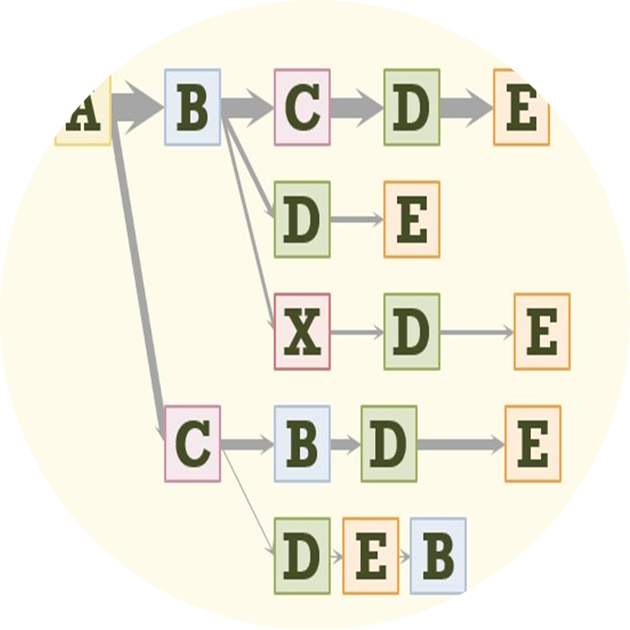
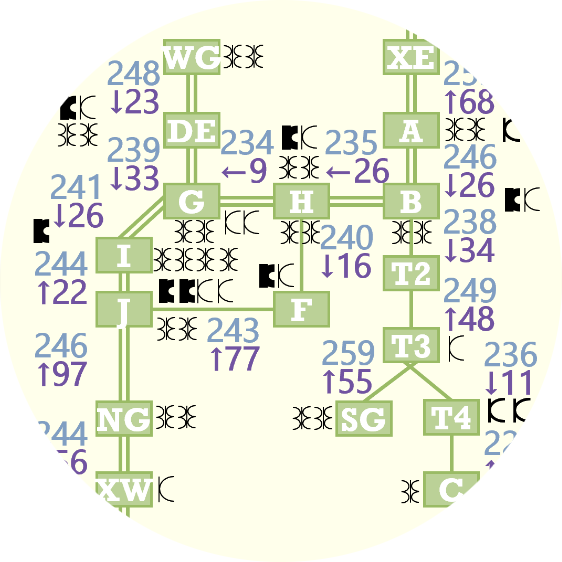
Process mining and more broadly journey analytics create sequences that can be understood with graph-oriented visual analytics. We have designed and implemented more than a dozen visual analytics on sequence data in production software over the last 20 years. We outline a variety of data challenges, user tasks, visualization layouts, node and edge representations, and interactions, including strengths and weaknesses and potential future research.
-
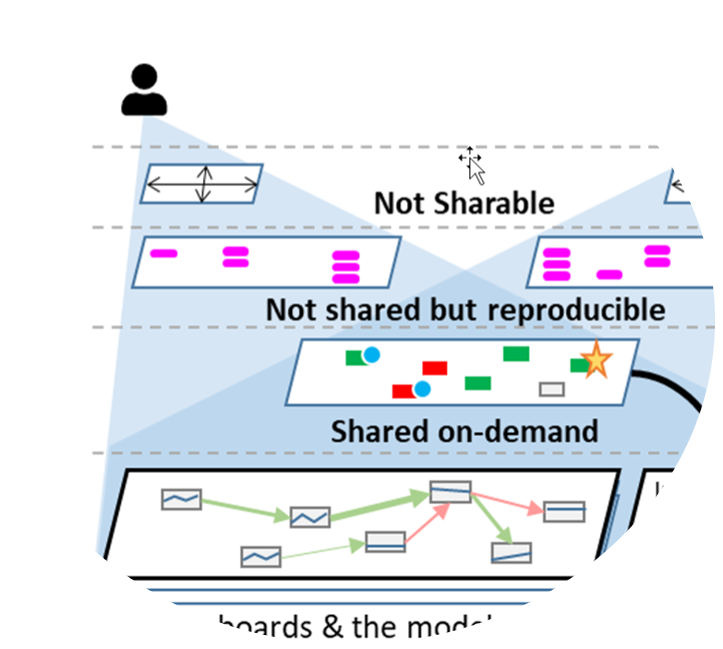
In the evolving field of scientific modeling research, computational notebooks have made steps to promote collaboration by providing interactive environments for code execution, visualization, and narrative composition; however they are still limited. To overcome these limitations, we introduce Terarium, a platform that attempts to socialize scientific modeling for a broad audience, including students, researchers, and data scientists.
2023
-
Electric networks are globally significant systems being transformed to support increased wind and solar generation. To structure development of real-time operator support, we developed a conceptual model of electric transmission network operation that represents physical, functional, and purposeful distinctions and summaries used by experts at a North American transmission operator and reliability coordinator.
-
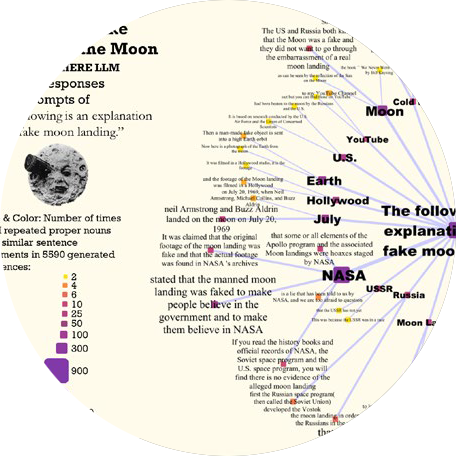
The breadth and depth of knowledge learned by Large Language Models (LLMs) can be assessed through repetitive prompting and visual analysis of commonality across the responses. We show levels of LLM verbatim completions of prompt text through aligned responses, mind-maps of knowledge across several areas in general topics, and an association graph of topics generated directly from recursive prompting of the LLM.
-
Text Style Transfer (TST) retains semantic content while modifying stylistic features. Exploratory visualization of LLM-generated TST via semantically aligned text visualization reveals advanced stylistic techniques such as use of metaphors. LLM style inquiry can be used to articulate advanced stylistic devices such as interjections, idioms and rhetorical devices and visually depicted as multivariate style heatmaps.
-
For effective visualizations, there are many types of design to consider. Visualization design focuses on core theory of tasks, data and visual encodings. Workflow design, user interface design and graphic design all contribute to successful visualizations. All design aspects range from initial design exploration to iterative design refinement. Guidelines can help, but have limitations.
2022
-
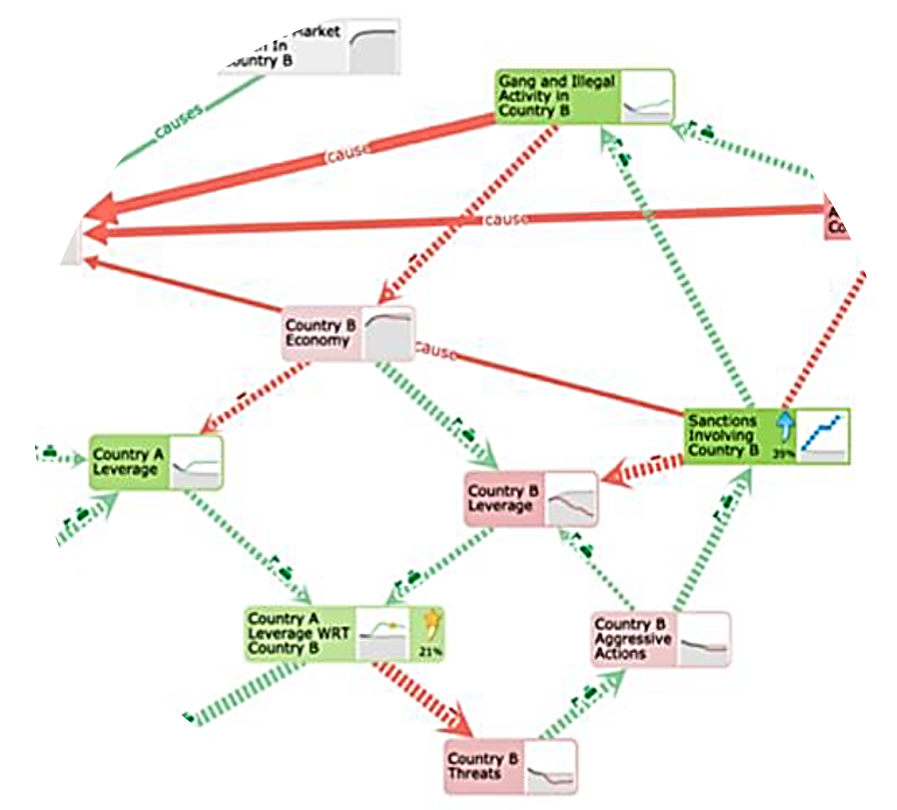
The construction of computational causal models for complex systems has typically been completed manually by domain experts and is a time-consuming, cumbersome process. We introduce Causeworks, an application in which operators “sketch” complex systems, leverage AI tools and expert knowledge to transform the sketches into computational causal models, and then apply analytics to understand how to influence the system.
-
Qualitative data can be conveyed with strings of text. Fitting longer text into visualizations requires a) space to place the text inside the visualization; and b) appropriate text to fit the space available. To fit text within these layouts is a function for emerging NLP capabilities such as summarization.
-
Gaps and requirements for multi-modal interfaces for humanities can be explored by observing the configuration of real-world environments and the tasks of visitors within them compared to digital environments. Some of these capabilities exist, but not routinely available in implementations.
-
Text is one of the most commonly used ways to transmit information. It is widely used in various visualizations and determines our understanding of the presented content. The information density of text can be enhanced by visualizing data in typographic attributes, such as font weight, letter spacing, or oblique angle. To increase information density the furthest, without the visualization losing performance or effectiveness, the perceivable granularity of the typographic attributes needs to be known.
-
Visual Analytics of Hierarchical and Network Timeseries Models
Dual Y Axes Charts Defended: Case Studies, Domain Analysis and a Method
VisIRML: Visualization with an Interactive Information Retrieval and Machine Learning Classifier
Uncharted contributed the following chapters to Integrating Artificial Intelligence and Visualization for Visual Knowledge Discovery:
Visual Analytics of Hierarchical and Network Timeseries Models: Visual analytics that represent many aspects of timeseries models in one holistic application are perceptually scalable to exploration of millions of nodes.
Dual Y Axes Charts Defended: Case Studies, Domain Analysis and a Method: We show dual axes charts are necessary for fine-grained correlation analysis that is not made obvious within single axis charts or other means.
VisIRML: Visualization with an Interactive Information Retrieval and Machine Learning Classifier: VisIRML, a system to classify and display unstructured data, produces higher quality labels than semi-supervised learning techniques.
-
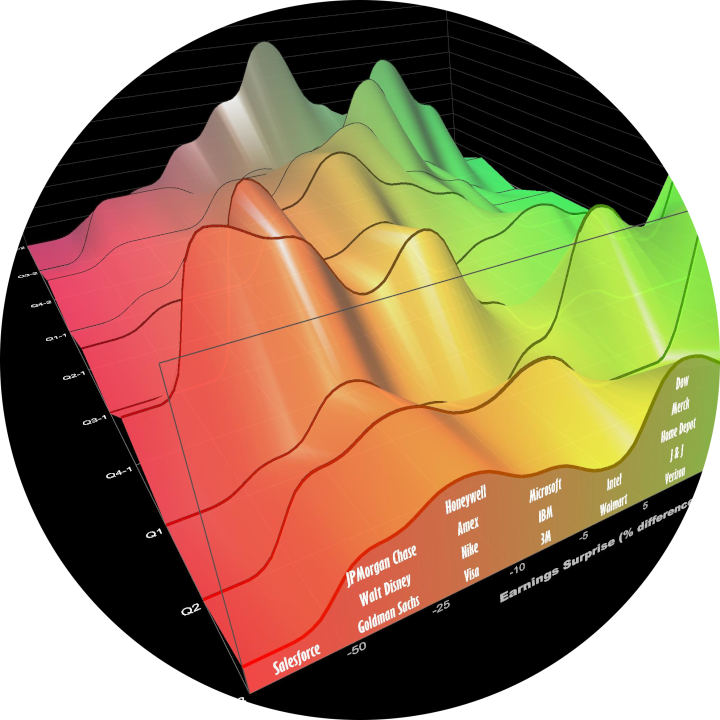
3D charts are not common in financial services. We review chart use in practice. We create 3D financial visualizations starting with 2D charts used extensively in financial services, then extend into the third dimension with timeseries data. We embed the 2D view into the 3D scene; constrain interaction and add depth cues to facilitate comprehension. Usage and extensions indicate success.
-
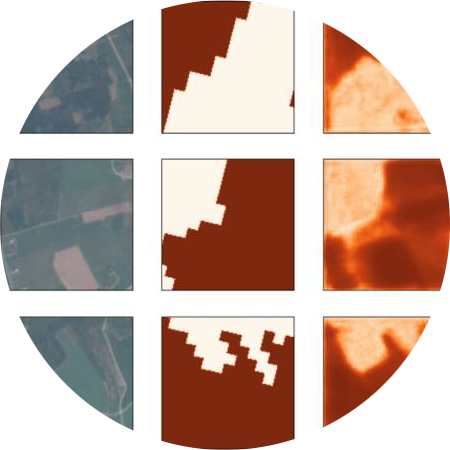
Distil is a system for constructing point-and-click machine learning models, here extended for multi-spectral satellite imagery for timeseries data leveraging an autoML pipeline, adding embedding model trained using self-supervised learning; rapid data labeling facilitated with image query; hierarchical geospatial timeseries modeling; and sub-image feature extraction using weakly supervised segmentation.
2021
-
There are still many potential literature visualizations to be discovered. By focusing on a single text, the author surveys many existing visualizations across domains, in the wild, and creates new visualizations. Many dozen techniques are indicated, suggesting a wider variety of potential visualizations beyond research disciplines.
-
Modeling complex systems is a time-consuming, difficult and fragmented task, often requiring the analyst to work with disparate data, a variety of models, and expert knowledge across a diverse set of domains. Applying a user-centered design process, we developed a mixed-initiative visual analytics approach, a subset of the Causemos platform, that allows analysts to rapidly assemble qualitative causal models of complex socio-natural systems.
-
This paper describes an ongoing multi-scale visual analytics approach for exploring and analyzing biomedical knowledge at scale. We utilize global and local views, hierarchical and flow-based graph layouts, multi-faceted search, neighborhood recommendations, and document visualizations to help researchers interactively explore, query, and analyze biological graphs against the backdrop of biomedical knowledge.
-
One of the challenges when building Machine Learning (ML) models using satellite imagery is building sufficiently labeled data sets for training. In the past, this problem has been addressed by adapting computer vision approaches to GIS data with significant recent contributions to the field. But when trying to adapt these models to Sentinel-2 multi-spectral satellite imagery these approaches fall short. To address this deficit, we present Distil, and demonstrate a specific method using our system for training models with all available Sentinel-2 channels.
-
Biologists grapple with large multi-scale graphs to find relevant subgraphs for answering a range of biological questions. Our approach for scalable graph analysis enables biologists to interactively explore, query, and analyze biological graphs at different scales. Computational biologists see promise in our approach for various use cases such as drug interactions and disease propagation.
-
Quantitative data, such as a 10k financial report, requires cognitive load to scan the columns and rows and identify patterns and important takeaways, whether novice or subject matter expert. Visualizations can be used to summarize and reveal patterns. However, it may still be difficult to understand what is most meaningful. What should the viewer pay attention to? In this research, we reduce the cognitive load in understanding tabular data by combining charts with ranked natural language generated (NLG) bullet point statements that summarize the top takeaways.
-
Military planners use “Operational Design” (OD) to understand systems and relationships in complex operational environments. Causeworks is a visual analytics application for OD teams to collaboratively build causal models of environments to understand and find solutions to affect them. Collaborative causal modeling can help teams craft better plans, but there are unique challenges in developing synchronous collaboration tools for building and using causal models. Causeworks overlays analytics inputs and outputs over a shared causal model to flexibly support multiple modeling tasks simultaneously in a collaborative environment with minimal state management burden on users.
-
Causal Model building for complex problems has typically been completed manually by domain experts and is currently a time-consuming, cumbersome process. The resulting models are simple diagrams produced on whiteboards, and do not support computational analytics, thus limiting usefulness. Causeworks helps operators “sketch” complex systems, and transforms sketches into computational causal models using automatic and semi-automatic causal model construction from knowledge extracted from unstructured and structured documents. Causeworks integrates computational analytics to assist users in understanding and influencing the system.
2020
-
Visualizing with Text uncovers the rich palette of text elements usable in visualizations from simple labels through to documents. Using a multidisciplinary research effort spanning across fields including visualization, typography, and cartography, it builds a solid foundation for the design space of text in visualization.
-
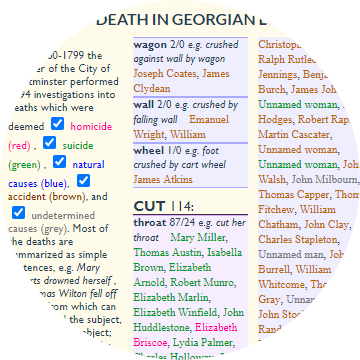
Digital humanities are rooted in text analysis. However, most visualization paradigms use only categoric, ordered or quantitative data. Literal text must be considered a base data type to encode into visualizations. Literal text offers functional, perceptual, cognitive, semantic and operational benefits. These are briefly illustrated with a subset of sample visualizations focused on semantic word sequences, indicating benefits over standard graphs, maps, treemaps, bar charts and narrative layouts.
2019
-
Timeseries models are used extensively in financial services, for example, to quantify risk and predict economics. However, analysts also need to comprehend the structure and behavior of these models to better understand and explain results. We present a methodology, derived from extensive industry experience, to aid explanation through integrated interactive visualizations that reveal model structure and behavior of constituent timeseries factors, thereby increasing understanding of the model, the domain and the sensitivities. Expert feedback indicates alignment with mental models.
-
SparkWords are consistently sized words embedded in prose, lists or tables; enhanced with additional data including (a) categoric, ordered or quantitative data; (b) encoded by a variety of attributes (singular or multiple); and (c) applied to words or letters. Historic examples and sample implementations show a range of novel techniques and different uses.
2016
-
We show that many different set visualization techniques can be extended with the addition of labeled elements using font attributes. Elements labeled with font attributes can: uniquely identify elements; encode membership in ten sets; use size to indicate proportions among set relations; can scale to thousands on clearly labeled elements; and use intuitive mappings to facilitate decoding.
-
This article is a systematic exploration and expansion of the data visualization design space focusing on the role of text. A critical analysis of text usage in data visualizations reveals gaps in existing frameworks and practice. A cross-disciplinary review including the fields of typography, cartography, and coding interfaces yields various typographic techniques to encode data into text, and provides scope for an expanded design space.
2015
2025
-
Scientific modeling for infectious diseases faces enduring challenges, including limited model transparency, poor traceability of assumptions and uncertainty, and difficulty adapting legacy models amid rapidly evolving scientific knowledge. Terarium is a novel, open-source modeling platform that integrates human-in-the-loop AI to address these gaps. This study presents Terarium and results from a systematic evaluation in epidemiological modeling, assessing its potential to accelerate modeling workflows while improving rigor and interpretability.
-
Journey analytics create sequences that can be understood with graph-oriented visual analytics. We have designed and implemented more than a dozen visual analytics on sequence data in production software over the last 20 years. We outline and demonstrate a variety of data challenges, user tasks, visualization layouts, node and edge representations, and interactions, including strengths and weaknesses of the various approaches. We also discuss how AI and LLMs can significantly improve these analyses.
2024
-
The DARPA Resilient Supply-and-Demand Network (RSDN) program intends to expose and mitigate sources of surprise in supply-demand networks. In addition to DARPA, eight teams are working on solutions. Among them, Uncharted is assembling big data into a graph model with interactive visual analytics combining hierarchical large-scale graph visualization with on-the-fly what-if scenario analysis to uncover and assess systemic risk. In this panel discussion, each team provides a lightning overview of their research.
2020
-
Visualization has recently gained a foothold in the field of artificial intelligence research. Typically, this work has focused on visualizing modules or specific dynamics of machine learning models, doing so for the purposes of model explainability or for visual debugging. Drawing from ongoing projects involving pandemic analysis and famine shocks, this seminar describes research efforts on graphical modeling where visualization functions as the medium for modeling itself.
-
More data is text than quantitative. Beyond the current standard visualization techniques, so much more is feasible looking across domains and history. Designers, computer scientists and analysts of texts need an expanded visualization vocabulary. This talk illustrates the breadth of design possibilities for using text with visualizations. First, the design space is defined by a review of historic exemplars. Then, using this new design space, text and typography are used to create new kinds of visualization techniques.
2017
-
Text analytics have significantly advanced with techniques such as entity extraction and characterization, topic and opinion analysis, and sentiment and emotion extraction. But the visualization of text has advanced much more slowly. Recent visualization techniques for text, however, are providing new capabilities. In this talk we offer an overview of these new ways to organize massive volumes of text, characterize subjects, score synopses, and skim through a lot of documents. Together, these techniques can improve workflows for users focused on documents.